Why invest in Nigeria?
What you need to know about investing in Nigeria
NIGERIAN ECONOMY
The Nigerian economy became the largest African economy following the 2013 GDP rebasing exercise by the National Bureau of Statistics. The rebasing included previously uncounted industries like telecoms, music, airlines, online sales, information technology and film production; bringing the GDP to a total of N81 trillion.
The Nigerian petroleum sector alone accounts for about 90% of the country’s total export earnings. According to data from the US energy Information Administration, Nigeria is the thirteenth largest producer of crude oil with 2.4 million bbl/day in 2013 and has the 2nd largest crude oil reserves in Africa, with 37.2 billion barrels and natural gas reserves of 5.12 billion cubic metres contributing 2.98% of the world total, according to OPEC statistics (PWC Doing Business Guide Nigeria 2015).
SOCIO-POLITICAL, ECONOMIC, ENVIRONMENTAL AND GEOGRAPHICAL FACTS ABOUT NIGERIA
| INFORMATION | DESCRIPTION |
| Official name | Federal Republic of Nigeria |
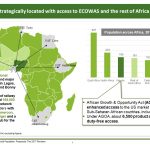
| Location | West Africa |
| Federal States | Nigeria is divided into 36 administrative divisions (States) and one Federal Capital Territory. |
| Capital | Abuja |
| Area | 923,768.64 Sq.Km. |
| Population | 178 million (2014 WB) |
| Population growth | 3.0% (2013 estimate, NBS) |
| Life expectancy at birth | 52 years (2013 WB) |
| Ethnic Groups | Over 250 |
| Religious Groups | Christianity (mostly in the South), Islam (mostly in the North) and Traditional beliefs. |
| National Day | October 1st |
| Official Language | English |
| Other Major Languages | Hausa, Igbo and Yoruba |
| Mortality rate, under-5 (per 1, 000 live births) | 117.4 (2013 WB) |
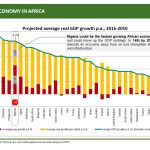
| GDP growth | 6.3% (2014 WB) |
| GDP (Expenditure approach) | N81 trillion (2013 NBS) |
| Inflation | 8.5% 1st quarter (2015, CBN) |
| International Memberships | Including, amongst others, ACP (Africa, Caribbean and Pacific States), AU (African Union), Commonwealth, Economic Community of West-African States (ECOWAS). (FMI). |
| Organizations | Economic Community of West-African States (ECOWAS); International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD); International Fund for Agricultural Development (IFAD); World Trade Organization (WTO). (FMI). |
| Commercial Cities | Lagos, Kano, Port Harcourt, Warri, Kaduna, Onitsha, Ibadan, Aba, Maiduguri (FMI). |
| Main Airports | Abuja, Lagos, Port-Harcourt, Kano, Enugu |
| Road Network | Over 194,200km (FMI). |
| Inland Waterways | 8,575Km (FMI). |
| Rail Network | 4,332Km (FMI). |
| Principal Rivers: | Niger and Benue |
| Currency | Naira (NGN) and Kobo(k): NGN1.00 = 100k |
| Vegetation: | Mainly Forest and Savannah |
| Climate: | Humid sub-tropical: with wet season from April to October and dry season from November to March. |
| Legal System: | Based on English Common Law and Customary Law. |
| Weights & Measures: | Metric System |
| Natural Resources: | Petroleum, Tin, Columbite, Iron Ore, Coal, Limestone Lead Zinc, Natural Gas. |
| Cash Crops: | Cocoa, Cassava, Ground nut, Kolanut, Palm Produce, Cashew Nut. |
| Major Industries | Crude Oil, Coal, Tin, Columbite, food processing, palm oil, peanut, textiles, cotton, rubber, wood, hide and skin, building materials, footwear, chemicals, printing, ceramic steel. |
| Main Trading Partners: | UK, US, China, Brazil and the European Union (FMI). |
| Climate | Varies; equatorial in south, tropical in centre, arid in north. |
| Terrain: | Southern lowlands merge into central hills and plateaus; mountains in southeast, plains in north. |
| Natural resources: | Petroleum, Tin, Columbite, Ironore, Coal, Limestone, Lead, Zinc, Natural Gas, Hydropower, Arable Land |
| Natural hazards: | Periodic droughts |
| Environment – current issues: | Soil degradation; rapid deforestation; desertification; recent droughts in north severely affecting marginal agricultural activities. |
| Mobile cellular subscriptions (per 100 people) | 73.3 (2013 WB) |
| Internet users (per 100 people) | 38 (2013 WB) |